Project Title : BzChair
Group Members
Ehtisham Anwar (BSE213173)
Mudassir Ali (BSE213005)
Supervisor Name: Mr. Ibrar Arshad
Project Description
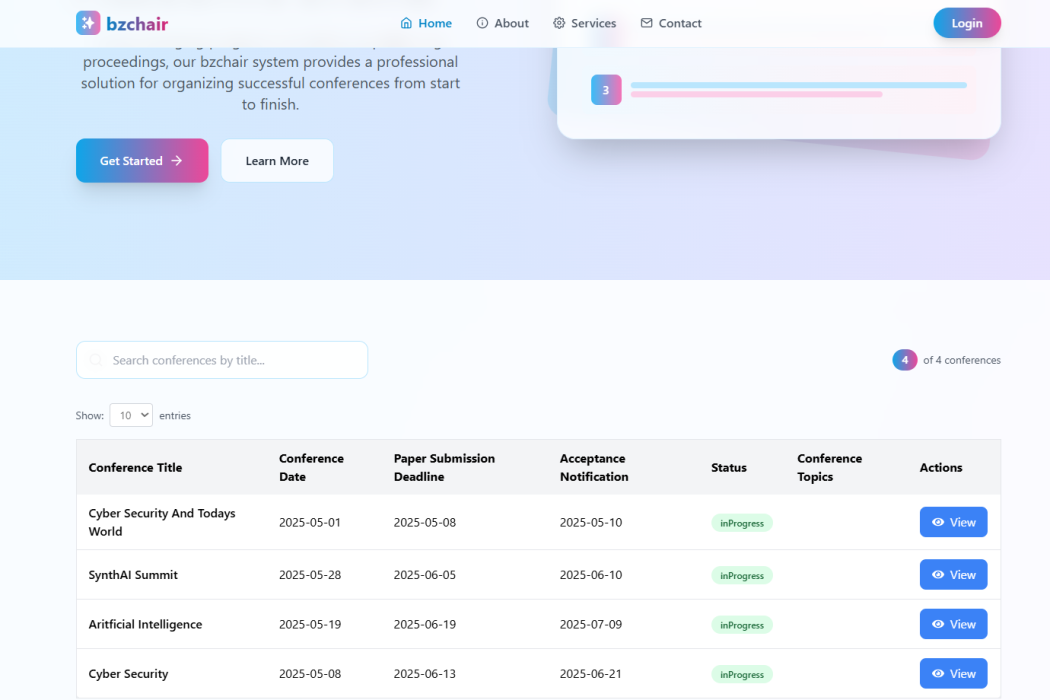
BzChair is a comprehensive web-based platform designed to simplify the management of academic and professional conferences. The system provides a centralized environment for organizers, authors, reviewers, and administrators to collaborate efficiently. It automates essential processes such as paper submission, peer review management, reviewer assignment, scheduling, and result announcements. Organizers can easily track submissions, manage sessions, and communicate with participants. Reviewers can review papers online using an intuitive interface, while authors receive real-time updates about their submission status. The system aims to eliminate manual tasks, reduce administrative workload, and ensure transparency throughout the conference lifecycle.
Features
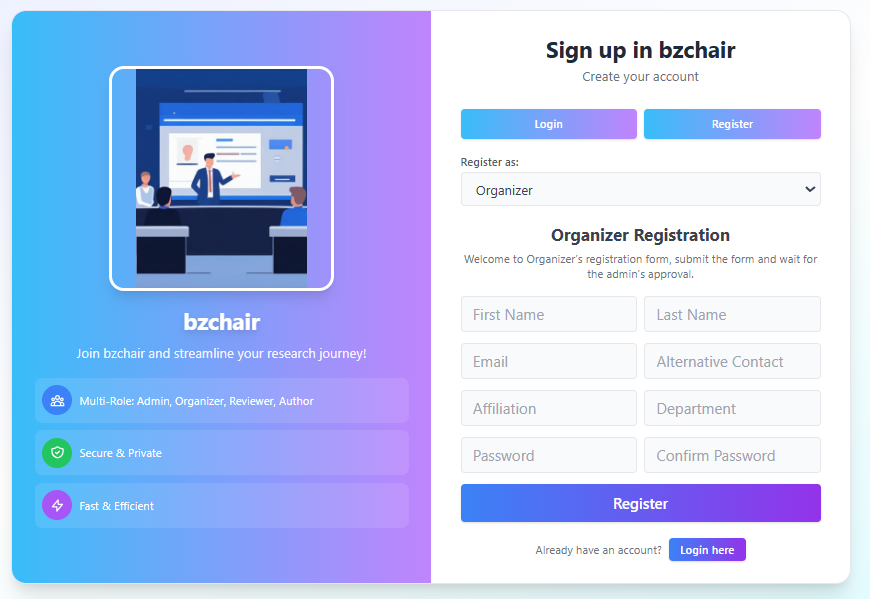
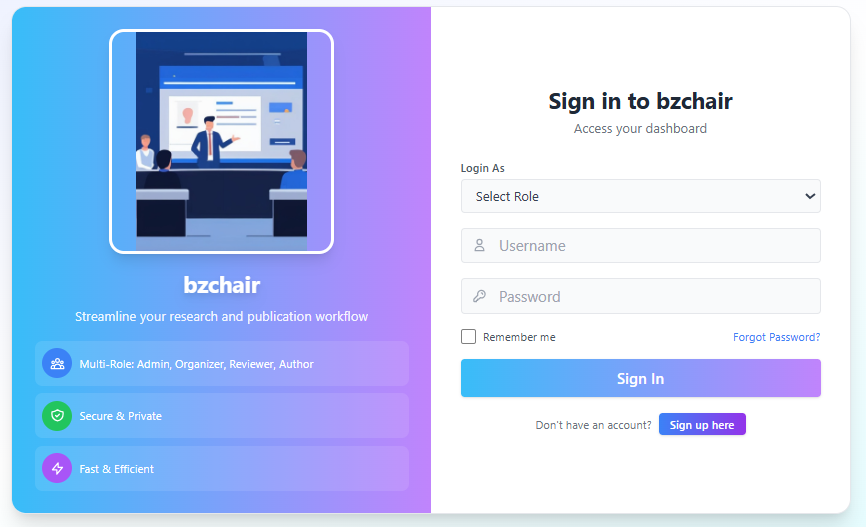
- Secure registration and login for all user roles (Admin, Organizer, Reviewer, Author)
- Paper submission and file management system
- Automated reviewer assignment and review submission
- Real-time conference dashboard with statistics and progress tracking
- Session scheduling and management tools
- Notifications and status updates for authors and reviewers
- Admin control panel for managing users and conferences
- Multi-language support (English and German)
Unique Features
- Role-based dashboards with distinct functionalities
- Sub-organizer support for review request management
- Integration with Strapi CMS for flexible content and backend management
- PostgreSQL for robust and reliable data storage
- Cloud-hosted backend ensuring scalability and availability
- Future-ready design for blockchain-based certificate verification
Technical Description
The BzChair system is developed using React.js as the frontend framework with JavaScript for dynamic and interactive interfaces, styled using Tailwind CSS for responsive design. The backend is powered by Node.js and Express.js, integrated with Strapi as a headless CMS to manage conference data efficiently. PostgreSQL serves as the main database for reliable and structured data storage. The system follows the MVC architecture, ensuring modular and maintainable development. Hosted on a cloud platform (such as Vercel or Render), BzChair ensures scalability and seamless performance. The system can be accessed from any device with a modern web browser and internet connectivity, requiring only standard hardware resources.
Host URL
https://www.bzchair.org/
Project Title : Design and Development of Parabolic Trough Solar Collector For Enhanced Thermal Performance
Group Members
Abdullah Rahman (BME 213002)
Zaryab Ahsan Shah (BME 213007)
Supervisor Name: Dr. Muhammad Irfan
Project Description
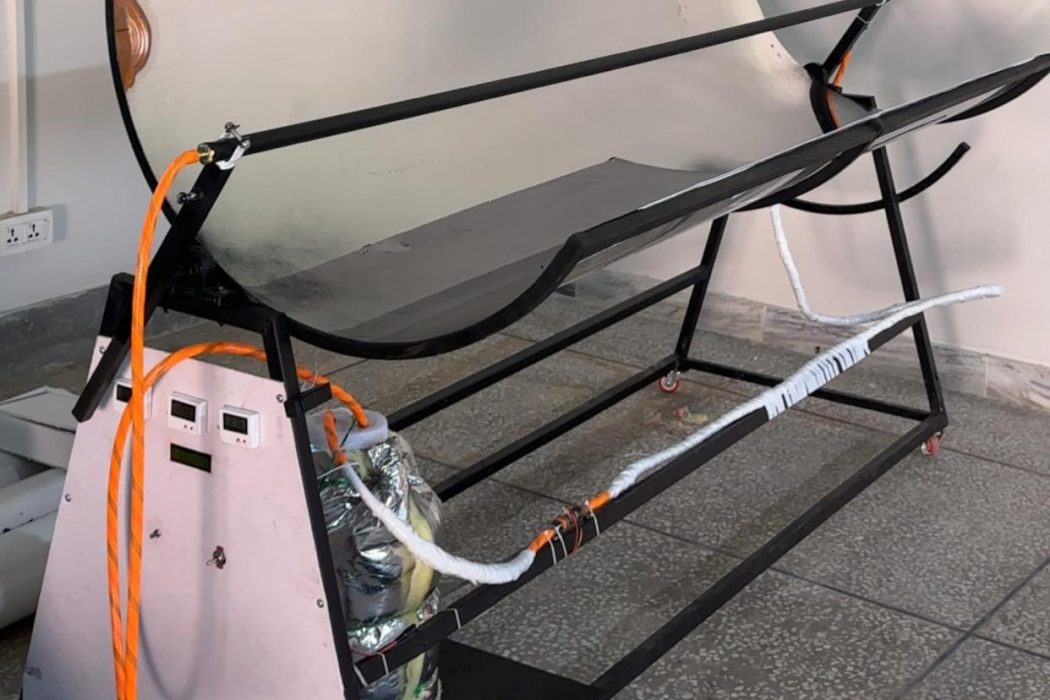
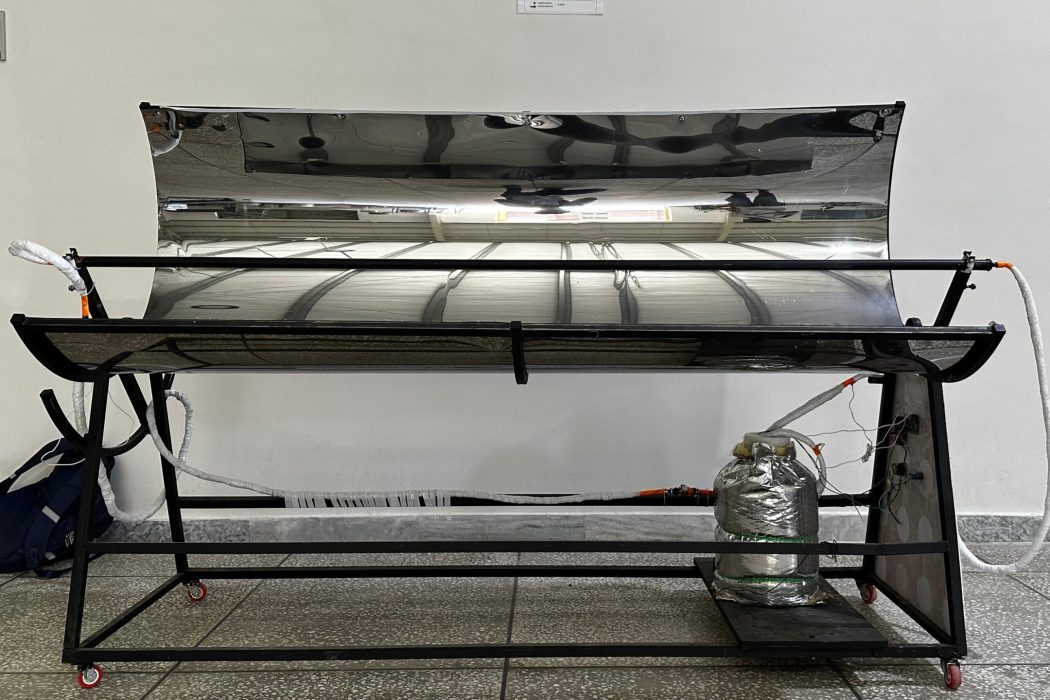
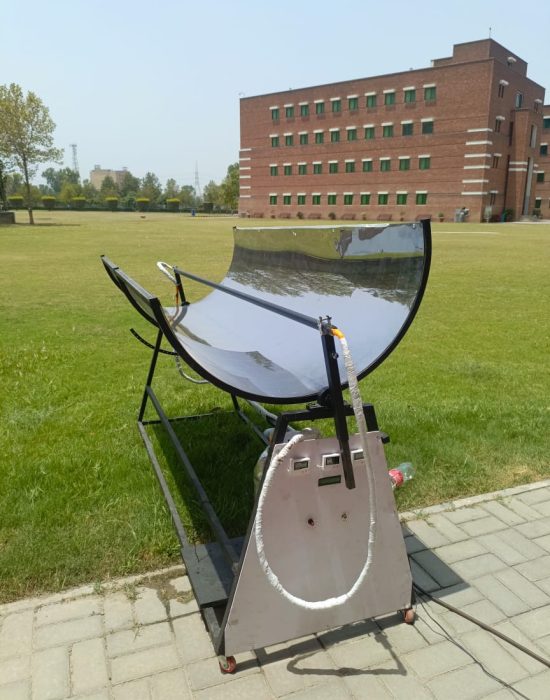
The project focuses on Parabolic Trough Collectors (PTCs), a solar energy technology utilized for heating purposes in areas with high solar radiation, providing a renewable, clean, and sustainable energy resource to replace conventional fuels. The development of these PTCs is a step towards sustainable development, aiming to reduce the environmental impact of traditional energy sources. The primary objective is to improve the performance and efficiency of the device while developing a feasible solution using cost-effective techniques. The project is aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those concerning clean energy, climate action, and sustainable innovation. Efficiency enhancement methods include the use of black painted copper tube to increase the thermal conductivity.
Features
- Electricity Generation: PTCs are widely used in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants to concentrate sunlight, heating a fluid that then produces steam to drive a turbine and generate electricity.
- Industrial Process Heating: The system provides high-temperature heat for a wide range of industrial applications, including food processing, chemical production, cement manufacturing, drying, pasteurization, and distillation.
- Desalination: PTCs supply the necessary thermal energy for distillation processes in desalination plants, converting seawater into fresh water.
- Centralized Heating Systems: In certain regions, they are utilized in heating systems to provide hot water or steam to multiple buildings, offering a solar-powered alternative to fossil fuels for centralized heating.
- High Efficiency: The design achieves higher overall performance compared to non-concentrating solar technologies due to concentrated solar radiation and minimized heat losses from smaller absorber surface areas.
Unique Features
- Optimized Receiver Tube Material: Utilizes copper tubes for the receiver, which are preferred for their superior thermal properties, and coats them with a black selective surface to maximize the absorption of solar energy and minimize heat loss.
- Reflector Coating for Enhanced Capture: Employs silver or aluminum reflective coatings on the parabolic mirror to maximize the amount of solar radiation captured, thereby boosting efficiency.
- Single-Axis Solar Tracking: Implements a single-axis movement mechanism which aligns the trough along an east-west direction, allowing the collector to track the sun from sunrise to sunset to maximize solar energy collection.
Technical Description
Hardware:
The collector’s core hardware consists of a parabolic chromium sheet reflector with an Aperture Area of 1.6 m² and a Concentration Ratio of 8.62. This focuses sunlight onto a black-coated copper receiver tube where the Heat Transfer Fluid (water) circulates. The system is mounted on a rigid frame utilizing a single-axis tracking system for alignment. Fluid circulation in the closed circuit is handled by a 12V DC pump, with a Variable Resistor used for flow rate control. Performance is monitored using a Digital Flowrate meter and multiple temperature sensors placed at the tube’s inlet, outlet, and inside the insulated storage tank.
Software:
The design phase involved developing a CAD model and simulation using SolidWorks to compare theoretical calculations with simulation results. All experimental data, including readings from the flow rate and temperature sensors, as well as ambient temperature, are continuously recorded and maintained in a data sheet using Microsoft Excel for detailed analysis.




